Hyderabad is an exciting city. It has a rich history. It is also modern and always changing. You can see cool old places.
it’s cultural landmarks and cutting-edge technological advancements. Once again, Hyderabad, the vibrant city in southern India, invites one to come and get acquainted with its colorful past, culture, and modernity which is the city’s essence. ,` is a unique combination of sacred and modern values conceptualized within the heart of Hyderabad, the Indian capital of Telecom and IT industries, where the Musi flows. The city, a reminder of its glorious past through its historic monuments like the Charminar to the recent IT hubs which add dynamism and diversity to its skyline, represents the trend of the State of Hyderabad. Through this article, we cross all feelers of Hyderabad, ranging from its captivating heritage to growing industries and thumping urban life The city of the Qutb Shah dynasty’s king Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah – the founder of Hyderabad, was established in 1591 CE. It was well arranged around the Charminar, which was the main architectural construction of the city. Hyderabad became famous as King’s Pearl and diamond trade center, also a cultural center.
HISTORICAL FACTS OF HYDERABAD
Hyderabad remains the city of history whose past urban history is embedded in every footstep and ancient buildings very well. The town was founded in 1591 by Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah, who selected the riverside site and named it “Bahadurgauda”. Over the decades the city monitored the start and the end of the dynasty that were considered the rulers of the rich. Nizams were the residents of the town, as it was their capital. The display of the city’s rich heritage is the intrusion of the architecture of the old sites, including Charminar and Golconda Fort, which are the symbols of the older history. The last 187 years have been rendered as the Crown capital of the Asaf Jahis by Hyderabad from 1769 to 1948. Previously, Hyderabad was the capital city of the Hyderabad princely State, and the seat of British Residency and cantonment until India gained independence from British rule in 1947.
INDUSTRY OF HYDERABAD
Hyderabad is the industrial capital of southern India and a true picture of the country’s growing economic strength having transformed from a mere agro-base to a leading industrialized economy. The spectrum of industrial activities in the city is a bustling palette of novelty and business, comprised of ICT services and biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. Being well-equipped with suitable infrastructure and abundant skills for the workforce, Hyderabad has become one of the favorite choices for local and foreign businesses that aim to expand in the market. Its unique geographical position, along with the government’s supportive policies, is driving the ever-increasing lead of the city as an industrial headquarters worldwide. Healthcare, electronics, automobile, aerospace, and food and beverage sectors are the main manufacturing domains in Hyderabad.
FAMOUS TOURIST SITE OF HYDERABAD
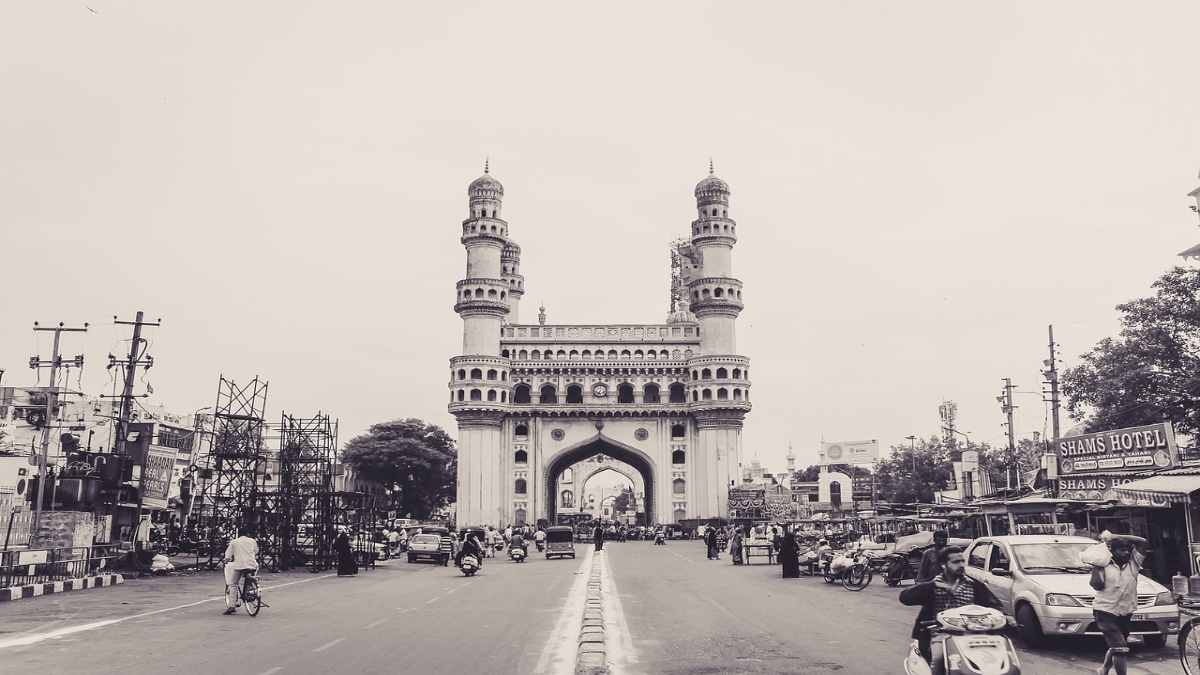
Uniquely engraved in the middle of the city, Charminar–the icon of Hyderabad, exemplifies the deep historicity and vigorous culture of the city. The fort was built in 1591, by Sultan Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah. It is a grand structure of buildings on four sides with towers on each side, depicting Islamic motifs in carvings and decorations. One cannot miss the crowds of visitors, who come to admire the impressive architecture and busy food markets inside it. The place feels so alive, one can taste and feel the sights, sounds, and flavors from the street markets. The buildings of cultural heritage in Qutb Shahi and Nizam style and Indo-Islamic structural designs continue to reflect influences from medieval, Mughal, and European styles which came into force after the flooding of the Musi river in 1908 when the city as we know it was built in and the civic monuments erected particularly under the reign of Mir Osman Ali Khan. His patronage of As late as 2012, An Indian government announcement honored Hyderabad as the “Best Heritage City of India” of all time. The architectural style of the 16th and the early 17th Qutb Shahi era was a Persian classical one; it was known for its domes, and colossal arches. The most ancient standing piece of architecture from the Hyderabad Qutb Shahi dynasty dating back to ‘the 15th century is ruined of the Golconda Fort. In fact, many of the historical bazaars, that are still in use, were constructed on this street, also near the fort. The Charminar iconized the city; at the center of the old part of Hyderabad, it is the square-shaped architecture with each side of 20m (66ft) and arches at the end facing the street. Taken separately, each side of the monument has a 56 m(184 ft) minaret. Charminar, Golconda Fort, and the Qutb Shahi tombs are well-known monuments in India. Defence Minister Mr. A.K. Antony declared in 2010 that the sites would be nominated for World Heritage status by UNESCO. This City has very beautiful tourist places to travel.
GEOGRAPHICAL BOUNDARY OF HYDERABAD
The geographical identity of Hyderabad, a state-of-the-art city located in the south of India, is shaped by a mix of various features that define this place’s uniqueness more profoundly. The capital of Andhra Pradesh, termed Hyderabad, is a city located on the Deccan Plateau, with the Musi River to the South and the Hussain Sagar Lake to the North. Eastern Ghats are enormous, green, and forested to the east. The tiered terrain from west to west is the Western Ghats on the western side. The unlimited geographical variety of Hyderabad not only provides for the awe-inspiring scenery but also affects the climate conditions and cultural traditions. Therefore, this variety guarantees endless curiosity for travelers and researchers. The Indian city of Hyderabad is 1566km (973 mi) from Delhi, 699km (434 mi) southeast of Mumbai, and 570km (350 mi) north of its destination. Telgange is located in the southern part of Telangana east of India. It lies alongside the Musi River, a tributary of the river Krishna River, which flows across the Deccan Plateau in the northern parts of Southern India. The area of about 650 km2 (about 250 sq mi) of Greater Hyderabad, a metropolitan area in India, makes it one of the largest metropolitan areas in India. It is Hyderabad’s average altitude of 542 m (1778 ft). The urban geography is both sloping and slightly hilly, with greyish and pink granite scattered with a few hills. The highest hill, titled Banjara Hills, has an altitude of 672 m (2139 ft). Moreover, as the city has many lakes at times mistakenly Examples are lakes made at the disrupting Musi river dams for instance Hussain Sagar, Osman Sagar, and Himayat Sagar. Although by 1996, the city had 140 lakes and 834 water tanks, the total population was still more than 1 million.
ADMINISTRATIVE PART OF HYDERABAD
The Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) oversees the civic infrastructure of the city, there are six administrative zones of GHMC: A zone of the South involves mostly Charminar whereas the main place of interest of the East Zone is L. A. (Nagar West SC), West Zone Hyderabad, which represents the city for its deep-rooted past and the cultural affluence, runs through an elaborate governing structure that manages the energetic city. Guiding all the operations is the Municipality of Hyderabad whose peripheral takes urban planning and civic amenities. Its functions cover different departments which operate daily to cater to public amenities services like supplying water, waste management, and construction of infrastructures. To the city’s governance relatively, HMDA, which is aimed at strategic planning and sustainable development is responsible. Taken together, the terms of the zonal bodies work ceaselessly ensuring the capital achieving great development and materialization of my very neighbor’s rich culture.–(Serilingampally), North Zone–(Kukatpally), Northeast Zone–(Secunderabad), and Central Zone–(Khairatabad); these zones include 30 ‘circles’, which in turn make up 1 Each ward has a corporator as a representative, elected in the popular vote. As of 2020, there are 7,400,000 voters in this town, with males constituting 3,850,000, and females fall in 3,500,000. The Corporators elect the political head Mayor of GHMC while executive power rests with the Municipal Commissioner who is state government appointed. The GHMC carries out the city’s infrastructural work such as building and maintenance of roads and drains, town planning including construction regulation, maintenance of municipal markets and parks, solid waste management, the issuing of birth and death certificates, the issuing of trade licenses, collection of property tax, and community welfare services such as mother and child healthcare, and pre-school and non-formal education THE GHMC was formed in April 2007 by merging the Municipal Corporation of Hyderabad (MCH) with 12 municipalities of the Hyderabad, Ranga Reddy and Medak districts covering a total area of 650 km2 (250 sq mi). Secunderabad Cantonment Board assumes the role of a local administration and governs an area of around 40.1 km2 (15.5 mi²). The territory is occupied by several military installations. The campus of Osmania University is run behind the institution’s autonomy. Gadwal Vijayalaxmi from TRS (Telangana Rashtra Samithi) is the mayor elected for the GHMC (Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation) in February 2021.
ECONOMICAL STRUCTURE OF HYDERABAD
Second to none Hyderabad is one of the biggest contributors to the southern Indian economy, showing it at the front seat in terms of economic prosperity where business comes alive through the streets and its diverse industry. At the base of the city’s wide sector network, an economy is rooted. Each sector adds to the cultural and economic landscape of the city. Hyderabad is home to a strong IT industry (with a world-famous Hi-Tech City), a thriving pharmaceutical and biotechnology sector, innovation, and growth in all its trysts. Furthermore, the city’s favorable geographical position and a good network of connections also are paired advantageously with its role as a significant investment route. The city has various sectors that host a wide spread of businesses hence, Hyderabad endures to pave the way as a leading economic center that not only contemplates domestic but foreign investments. Recent estimates of Hyderabad’s economy of the metropolitan area ranks fifth or sixth in the list of metropolitan areas in India which comes up with a GDP of $40 to $74 billion (PPP). In the list of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Hyderabad is rated 6th in the nation as deposits and 4th as credit, according to the data of June 2012. At the same time, Hyderabad is the most powerful contributor to the economic development of Telangana and its taxation income. Per capita annual income for the year 2011 was $550, the figure was ₹44,300. As indicated by a 2006 survey, the most significant employers of the city were the state government (113,098) and central government (85,155) employees. Overall, 77% of males and 19% of females in this industry were engaged in production. The service industry remains the strongest in the city and 90% of the employees here concentrate on this sector.
CULTURE & ARTS OF HYDERABAD
With Hyderabad, a city which is known for its historical and cultural heritages, its arts and culture scene will be beating strongly. The artistry of paint and stone characters is displayed in every nook and corner of historic Charminar and old markets. The cultural heritage of the city is manifested in the wide array of arts, like the ‘classical dance forms of the Ravindra Bharathi, or the immaculate handwork, and their products that are found in the city’s famous bazaars. The convergence of Mughal, Persian, and Telugu influences make Hyderabad a veritable cultural amalgamation greatly enhanced by the fact that every brushstroke and note from a musical instrument can narrate its rich history as well as evergreen present. As the massive Mughal Empire declined, Hyderabad was enthroned as the most important place of high culture in India. A mass migration of performing artists to the city marked an important turning point during the Nawab era, especially from north and west of the Indian subcontinent which were previously under the abundant patronage of the Delhi rulers. Though this influx itself caused the contact of North and South Indian languages cultures and traditions, Indian Islam and Muslim Islam have ever since been shared and the city is internationally and nationally popular for this coexistenceAs a result, the north-south mix sees the English language being used in the official protocols of Telangana besides the official use of Telugu and Urdu. The blending of different religions has been seen especially during the celebration of some festivals, for example, Ganesh Chaturthi, Diwali, and Bonalu belong to Hindu tradition, and Eid ul-Fitr and Eid al-Adha are celebrated by Muslims in a city where all of them co-exist. The tribal regularly dressed men were those adorned in sherwani, kurta–pajama, while women wore khara dupatta and salwar kameez. Most Muslim females are also found wearing burqa and hijab when they are outside, In addition, the trend of Westernization witnessed fresh highs when it comes to teens wearing Western clothes.
SEX RATIO & LITERACY RATE OF HYDERABAD
Unlike any other, Hyderabad, the vibrant capital city located in southern India, stands out in having its sex ratio and literacy rate that have pushed it to the top. A larger metropolis indicates the city has a sensible proportion of both sexes and by this, the policymakers can sense the state of social advancement in the city. Alongside it, the sex ratio is now a favorable ratio of 945 females to 1000 males, implying a balanced gender representation. Additionally, the city also emphasizes its relatively high literacy rate, which exceeds the national average. With roughly 83% of its population being literate, the city has made any form of education and outright empowerment possible by endorsing that poetic position as the lighthouse of betterment in its surrounding territory. Education Rate of Hyderabad- Lines of Songs and DancingHyderabad’s average literacy rate is 83.26 percent of which male is 87.31 and female literacy rate is 79.04 percent. There is a 1,000: 955 sex ratio in Hyderabad city, which is more males than females. The world sees 7 girls born per 10 baby boys among the sex ratio of children.
POPULATION GROWTH & POPULATION DENSITY OF HYDERABAD
The Greater Hyderabad area has witnessed over the past years rapid population growth as well as population density in recent years. On account of being one of India’s biggest cities, it has attracted a lot of migrants who are seeking economic bio opportunities as well as quality life. This has in turn contributed to the high rise in the country population leaving the city populous. Consequently, the increasing population density has been a reality in Hyderabad, where life in the residential and commercial areas is known to be crowded. Thus, the prevalent trend symbolically highlights the challenges and attractive perspectives that present to Hyderabad on sustainably maintaining its urban development. The total number of metro inhabitants in Hyderabad in 2024 as of the new data to surface is 11,069,000, a 2.48% upshot from 2023. The boom in the city’s population in 2023 was an estimated 10,801,000, a 2.53% increase from 2022’s 9,578,181. Hyderabad city of metro area in 2022 had a population of 10,434,000 and the increase was 2.58% from the last year.
CONCLUSION
The city of Hyderabad, derived from the name of the Qutb-ul-Mulk’s rebuilt fort and known for the pearl trade, is characterized by a unique blend of history, culture, and modernity providing the people with a different flavor. Its landmarks Charminar and Golconda Fort are clear manifestations of its glorious past. Also, the current scenario of this place where the streets and markets are full of life and activities is just a miracle. They range from exploring scrumptious Hyderabadi biriyanis to admiring the stunning architecture of its mosques that allows tourists to involuntarily internalize such experiences. Also, the fact that the town is filled with emerging tech businesses and IT parks is a testament to that city’s place on the global stage. In the end, Hyderabad visitors due to the perfect blend of tradition and novelty, offer a one-of-a-kind experience to everyone who visits.
1. Why is Hyderabad a favorite place?
Hyderabad grabs the eyes of people who visit. It has a long history that makes it special. It also has fun things to do and yummy food. Famous places like Charminar and Golconda Fort show what life was like long ago. Hyderabad still keeps some old ways but also has new things. People like going there. They like seeing the old and new things together. Hyderabadi biryani is the most tasty food there. Markets in the city are fun to walk through. They have lots of things to buy. Things in Hyderabad are unlike anywhere else. People who visit feel happy.
2. Why is Hyderabad famous?
Hyderabad is a city with lots of history. It has old buildings like the Charminar and Qutb Shahi Tombs. These places show how great the city was long ago. Hyderabad has a big movie business and many tech companies too. It also has busy markets where you can buy things. The city mixes old and new ways of life. This makes Hyderabad an exciting place to visit for people from all over the world.
3. What is inside Ramoji Film City?
The world’s biggest studio, Ramoji Film City, gives you a cool look at movies. It covers more than 2,000 acres and has huge sets, pretty gardens, and live shows. You can walk around movie sets, ride fun rides, and watch people act on stage. From nice spots to see behind the scenes, Ramoji Film City gives you an amazing movie experience you’ll never forget.
4. What is the nickname of Hyderabad?
Long ago, the place we know as Hyderabad was famous for its pearls. People called it the “City of Pearls” because many pearls and diamonds were traded there. The city was very important for selling these beautiful gems. For hundreds of years, Hyderabad was known as a place of great riches and luxury because of the pearl trade. Even though the pearl business is smaller now, Hyderabad’s culture and royal style still shine brightly. That’s why people still call it the “City of Pearls” today.
5. Who founded Hyderabad?
Hyderabad began many years ago. Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah started the city in 1591. He was the fifth leader of the Qutb Shahi family. Muhammad built Hyderabad on the southern side of the Musi River. He did this to celebrate the end of a very bad sickness. Under his rule, Hyderabad became a great place for culture, business, and art. This left a big mark on its history. It also shaped what Hyderabad is for many years after.