Discover the soul of Delhi in ‘Delhi Diaries’, where the echoes of Mughal emperors mingle with the rhythms of modern life, creating a symphony of heritage.
Delhi, as India’s vibrantly woven capital city, achieves a suitably delicate balance between the past and present. Sitting on the Yamuna River currents, this city reflects India’s past and present with lavish gifts of the future! From the splendid Mughal architecture of the Red Fort and the Jama Mosque to the enormous sky-scape at Connaught Place and Cyber Hub, Delhi effortlessly clothes itself in the past as well as the present-day aspirations. This city enjoys not only the support of the domestic population, but also people from all parts of India, and the world as well, which boosts the romantic vibe.
As the country’s epicenter of politics, Delhi vibrates with activity, with the government headquarters, the foreign Embassies, and the various international organizations situated there. Its impressive food scenery from lip-smacking street food to some of the best haute cuisine tantalizes taste buds and its food lovers. With the city’s never-ending markets, and festivals loaded with life and flourishing arts, there is nothing to be bored in Delhi this vibrant city.
On 12th December 1911, the British monarch George V of the British Empire solemnized a decisive event that conveyed the desire to move the capital of India from Calcutta to Delhi at the historic Delhi Durbar. The start of the metropolitan city of Delhi as the Capital of India, then the preparation for the building of a new city commenced with a great symbolizing regal splendor and Canadian flag stitching. Unearthing Delhi is not only traversing tourist places but also feeling the palpable vibe pervading each street which is epitomized by tales and every encounter that makes a proud person multi-fold.
HISTORICAL FACT OF Delhi
The many different types of cultural and historical heritage that the city of Delhi possesses which is very deeply rooted in the history of Delhi is the result of constant development throughout the ages. On the fringes of Yamuna, New Dehli had the chance to observe various happenings, affections, and developments. Not only does its historical heritage have millennia of history, but also existing vestiges of settlements dating back to the 6th century BC have been found. Throughout history, Delhi has been the capital of several empires. Some of these empires that had their capitals in Delhi were the Mughals and the British.
Therefore, Delhi is an embodiment of power, politics, and culture. Among its many historical points of interest is being the capital for various dynasties successively during its history from the Delhi Sultanate to the Mughals. Each leader contributed to shaping the culture of the city uniquely, leaving behind an undeniable heritage. Delhi from bygone times onwards has stood in the front row as a beacon, and its ancient monuments, lively shopping streets, and fascinating individual components have brought to reality a historical tale of past, present, and future that attract people to get immersed in its rich history. Hence, it was on the 12 of December (1911) that this charter was formally passed on.
In 1927 Delhi remained called New Delhi and the event of moving the capital was celebrated on 13th February 1931. New Delhi was insured as the capital of the Union of India in an official capacity on 15 August 1947 which followed the Independence of India.
INDUSTRY FACTS OF DELHI
As a bustling capital city that is alive with activity and emerges as a dynamo of industry in India, Delhi plays a very vital part in the country’s economic situation. With its status as the capital, Delhi acts as the capital of ever-changing industries with the industrial cluster that is responsible for economic progress and creation. From the innovative tribal craftsmanship to the contemporary IT and industrial sectors, Delhi’s industrial niche is just as encompassing as its cultural complexity. The establishment of the city in a strategic location with well-developed infrastructure has been the main factor for the businesses, local and international firms alike, to open up their businesses there and make the most of the opportunities for expansion and investment. Information technology, telecommunications, manufacturing, and retail depts seem to be predominantly present in the territory of Delhi with all of them being the key engines fueling the economic health of this megapolis. Besides that, Delhi’s growth as a startup and entrepreneur community’s CenterPoint has amplified its audio as a complex economic power. Deep with a vast scope of production and a conducive environment for businesses, Delhi brings a new destination to the pages of history, once more paving its way to the status of the biggest industrial city in the region.
FAMOUS TOURIST SITE OF DELHI
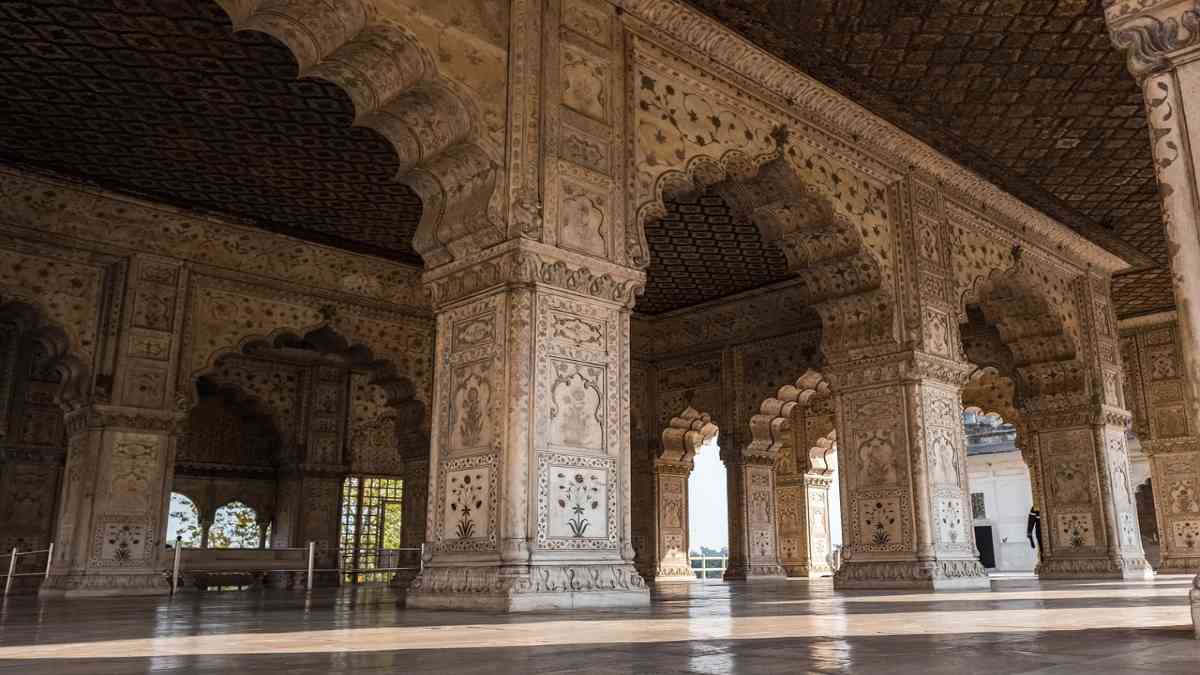
Delhi, a city with a mix of wonders, always makes travelers feel compelled to check out its spectacular set of tourist attractions. The kaleidoscope of experiences offered by Delhi ranges from intriguing ancient monuments to new-age marvels. This makes the place a favorite among different types of travelers. On the very center of this city stands a famous monument, The Red Fort; a UNESCO-protected site, whose deep red walls turn into a background of rapture and awe landing in stories of Mughal many-splendor. Within a short walk, we come to the Jama Masjid, a large mosque with domes and minarets that is an architectural masterpiece in India. With the strategic placement of travelers at the core of Delhi’s Old Market, marvellers are inevitably brought back to the overwhelming appeal of Chandni Chowk, where narrow ages-old bazaars are filled with irresistible street food and completely different attractive items.
You can relax with the charming view of the green landscape of Lodhi Gardens that come to your rescue in the heart of the city, with ancient tombs and verdant gardens bringing back tranquility into your life from the very ancient Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire during the 13th century till the present day. The Qutub Minar, Humayun’s Tomb, and Red Fort which constitute the UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Delhi built during that time and also facilitated the augmentation of cultural, economic, and social progress and well-being.
GEOGRAPHICAL BOUNDARY OF DELHI
Delhi the north-central city of India ranges between these latitudes-28°-24′-17″and 28°-53′-00″ and longitudes of 76°-50′-24″ and 77°-20′-37″. Delhi embraces measurement with the States of Uttar Pradesh and Haryana. The city of Delhi provides an area of 1,483 square kilometers. On the south is the Aravalli Range, its end of urban fringes that serve as the natural border while on the east is the vast floodplains of the Yamuna River which adds a green hue to the city surroundings. It may be an attractive city with so many things happening, but it will not be enough. There are sites of greenery with forests and parks scattered all over within the expansive urban space that would serve as a wildlife area with a slight reprieve from the urban concrete jungle. Being one of the most important parts of the northern part of India, the city of Delhi offers its amazing geographical boundary which is also a microcosm of the country’s diverse terrain that invites exploration and discovery at every end. On the one side of it, are neighboring states of Rajasthan and Haryana.
THE ADMINISTRATIVE PART OF DELHI
which, has an area of 539.5 sq mi. It is further divided into 12 zones: Center, South, West, Noida, Regor Garden, Vijay Vihar, Civil Lines, Karol Bagh, Sector 5, Pugnahpur, Shahdara North and Shahdara South. He is the current Mayor of the Unified Municipal Corporation of Delhi, elected one of them is the largest lake located at the city core with an area of 42.3 km2 (16.3 sq mi), which is bigger than the other one. Between 13 January 2011 and 22 May 2022, MCD was divided into three municipal corporations: had jurisdiction over South and West Delhi areas, including Mahipalpur, Rajouri Garden, Uttam Nagar, Badarpur, Jaitpur, Janakpuri, Hari Nagar, Tilak Nagar, Dwarka, Jungpura, Greater Kailash, R K Puram, Malviya Nagar, Kalkaji, Ambedkar Nagar and Pul pehladpur.) had jurisdiction over areas such as Badli, Rithala, Bawana, Kirari, Mangolpuri, Tri Nagar, Model Town, Sadar Bazar, Chandni Chowk, Matia Mahal, Karol Bagh, Moti Nagar. had control over the areas comprising of Patparganj, Kondli, Laxmi Nagar, Seemapuri, Gonda, and Babarpur along both bankers of River Yamuna. Delhi is Delhi High Court.
The Delhi High Court is the highest in Delhi from where the Supreme Court takes up the cases. High Court of Delhi just as the highest court and other courts in India is the court of record. Delhi is the court that in addition to the District Court has other courts with territorial jurisdictions. Currently, Delhi is the ruling seven District Courts namely Tis Hazari Court Complex, Karkardooma Court Complex, Patiala House Court Complex, Rohini Court Complex, Dwarka Court Complex, Saket Court Complex, Rouse Avenue Court, along with CBI Courts, Consumer Courts, Labour Courts, Revenue Courts, Army tribunals, electricity tribunals, Railway Tribunals, Delivering police service purposes Delhi is split into 15 police districts which are then further sub-divided in 95 local police zone. As of today, the Delhi police station tally stands at 180 stations.
ECONOMICAL STRUCTURE OF DELHI
Delhi is considered the biggest commercial center in the West. The resultant Delhi metropolis’s GDP, a combination of 2016 real prices and PPP conversion (PPP metro GDP), is either the leading or the second most producing urban area of India, with estimates ranging between $ 370 billion and $ 400 billion. The nominated GSDP of NCT of Delhi, for 2016-17 was estimated as ₹6,224 billion (US$ 78 billion) which was 13% higher than in 2015-16. The Economic Survey of Delhi (2005-2006) says that the tertiary sector contributes roughly 70.95% of Delhi’s total small development product whereas secondary and primary sectors contribute about 25.20% and 3.85% respectively.
The workforce constitutes 32.82 percent of the total population of Delhi; The figure rose by 52.52 percent from 1991 to 2001. Delhi’s Employment Rate fell from 12.57%during the time 1999-2000 and registered a rate of 4.63% in 2003. In December 2004, 636000 people were directly registered in the employment exchange systems of Delhi. In total, the workforce in 2018 in national and state governments and quasi-government was numbered 594 thousand, and the private sector employed about 273 thousand. The main services work getting done are in sectors like IT, telecommunications, hotels, banking, media, and tourism.
The construction, power, health, and social services, as well as real estate, are other significant parts of the city’s economy. Delhi boasts a vast and fast-developing retail industry that is next to the biggest in our country. Another factor that contributed to the city’s economic boost was the growth of the manufacturing sector as major customer goods companies set up their production units and established their headquarters within the city. Delhi’s high consumer-acceptable market and flexibility of skilled labor attracted foreign investment. Manuilture industry in the year 2001 employed 1,44 million employees and the city had 129 thousand industrial units.
CULTURE & Arts OF DELHI
Delhi has an outstanding culture that has been affected by events such as its long period and historic association as ‘India’s national capital’. It not only refers to the language which is dominated by the populous refugees with Punjabi influence but also to the clothing, and foods similar to those in Punjabi and still much to mention. The recent yet excessive migration from other parts of the families may promise to convert this place into a melting pot of minds and interests hence the much bigger melting pot which will be witnessed over time. This is seen with the many important monuments that are in the heart of the city.
ASI identifies 1,200 historic buildings and 175 monuments as heritage sites, recognized as national monuments status. The Mughals and Turkic dynasties contributed a lot to the beautiful architectural legacy of Delhi, the notable among them being the magnificent Jama Masjid- the largest mosque built in 1656[233] on the one hand and the Red Fort towards the opposite side. Delhi houses the popular sacred sites of the world such as Red Fort, Qutub Minar as well as the Humayun’s Tomb. Libraries, monuments such as the India Gate, the Jantar Mantar—an 18th-century astronomical observatory, and the Purana Qila—a 16th-century fortress are other significant structures. Laksminarayan temple, Akshardham temple, Gurudwara Bangla Sahib, Lakshminarayan temple, Lotus temple for the Baháʼí Faith, and the ISKCON temple are modern era architecture.
At Raj Ghat, memorials and related places of historical significance have been set up for Mahatma Gandhi and other important people. The capital of New Delhi is home to a great number of government buildings and officials’ residences (built in a colonial style that recollects the English times) including Rashtrapati Bhavan, the Secretariat, Rajpath, the Parliament of India, and Vijay Chowk. The Safdarjung Tombls serve as an example of the Mughal garden style. The vicinity of Old City has known some royal mansions, called havelis (big mansions), too. Lotus Temple is a popular prayer site of the Bahai Faith, built and completed in 1986. Notable for its flowerlike form, it was considered, in the past, the Mother Temple of the Indian subcontinent and has gained popularity over the years since people are prone to come and take a look at it. Provincial museums and contemporary art museums being the largest museums of the country are examples of it. Other famous museums in Delhi are the National Museum of Natural History, the National Rail Museum, and the National Philatelic Museum.
SEX RATIO & LITERACY RATE OF DELHI
Delhi, nicknamed ‘Dilli’, the lively and multicultural capital city of India, serves as the backdrop for a vivid scenario of the society through its sex ratio and literacy rate. Delhi whose city lines are full of shine despite what it grapples with, namely, gender imbalances represented in the female sex ratio. Nevertheless, with the endeavors for gender equality and girls’ empowerment, females’ status is just a little better than before. It is performed alongside other virtuous data like Delhi’s considerable literacy rate, which is a clear indicator of its devotion to education and human development. In the city, one will commonly note that the literate population is always above the national average. Here, the city will show itself as a lamp of knowledge and enlightenment due to the existence of numerous educational institutions such as extant prestigious universities, and grassroots initiatives among others.
The 2011 HRSE of the people in NCT of Delhi with the total population reaching 16,753,235. The just corresponding population density was 11,297 persons per km2 with a sex ratio of 866 women per 1,000 men and a literacy rate of 86.34%. In 2001, 285 thousand extra inhabitants moved to Delhi because of internal migration, and 215 thousand babies were born. Thus, Delhi became one of the fastest-growing cities in the world. Spreading over Asia’s largest planned residential area, Dwarka Sub City, located within the borders of the National Capital Territory of Delhi, is one of the most recent housing additions. The urban extension has made the Delhi metropolitan area dose to NCT borders to include such cities from neighboring states which are namely Faridabad, Gurgaon (Haryana) Ghaziabad, and Noida (UP). Moreover, the total population of these cities is very close to about 28 million people as per the estimation of the United Nations.
UN spokesperson claims that Delhi, as a metro area, overtakes Tokyo while Dermographia registers the Jakarta metro area within the second place. The 2011 census provided two figures for the urban area population: This works out to 16,314,838 for NCT and 21,053,486 for the Extended Metropolitan Area. The 2021 regional master plan however specified the area up to the city of Chandigarh, (which was earlier classified as the Delhi Metropolitan Area in the 2001 plan) instead of the Central National Capital Region (CNCR).
POPULATION GROWTH & POPULATION DENSITY OF DELHI
Delhi, the ‘engine’ of India, not only as India’s political and cultural capital but also as it passes its test, faces the duality of a rapidly growing population and a high density of population. As the years come and go, there is an increasing number of the city population, steered by the movement of inhabitants missing from villages and neighboring provinces for the bright city lights. Many people come to India’s capital with no jobs and few resources. These migrants allowed Delhi’s population to shoot up to overwhelming numbers, with huge pressure on existing infrastructure, resources, and services. Consequently, the city deals with high population concentration that will yield dense urban design with no space to spare, wherein the urban area will manifest as congested streets, full and compacted houses, and neighborhoods.
Notwithstanding all these difficulties, Delhi’s spirit of resilience remains undeterred, as it always keeps adapting and abelian to the fast-rising population. Through urbanization planning, transportation grid investments, and other plans that are intended to improve physical access, Delhi plans to deal with population growth as well as density while holding on as an attractive and diverse center of opportunities.
CONCLUSION
Lastly, Delhi is discovered as a city of two extremes and complex issues, where old legacy stands together with recent cutting-edge innovations and traditions that are kept up with current progress. A closer look at their busy streets full of buildings that have historical and cultural value confirms the richness of the past and walks them through the future dynamic and modern spirit. It is from the magnificence of the beautiful Red Fort to the calmness and tranquility of the Lotus temple that Delhi shows a textile of events that mesmerizes and remain intact in a person’s life. Along with being the political, economic, and cultural capital of India, Delhi also serves as the engine that turns the wheel of the nation’s destiny and identity on the world maps.
There are problems such as traffic jams that are ever present in every city. However, Delhi is the one city that still manages to develop and flourish because of the people’s resilience and creativity. It is true that it also has a lot of environmental issues to deal with. The capital is also symbolizing a bright future in which dreams come true and hopes are almost realized for everyone while the city culture offers vibrant, taking wings of aspirations.
1. When did Delhi become New Delhi?
On February 13, 1931, Delhi was officially declared New Delhi. This decision was in line with the British government’s plan to move the capital of British India from Calcutta (now Kolkata) to Delhi. The purpose of this change was to create a new modern administrative center equipped with infrastructure that reflected the importance of Delhi as India’s capital.
2. Who built Delhi city?
Delhi was established long ago, and various rulers made their contributions to its progress and development. This city, which dates back centuries, was the brainchild of Shah Jahan, a Mughal Emperor who mandated Shahjahanabad construction in 1638 making it the seventh city of Delhi. Modern-day Old Delhi was started from this city. It was once the Mughal Empire’s capital.
3. How is Delhi named?
Delhi got its name from the long ago-old name “Dhillika” or “Dhilli” which relates to the outdated city’s setup by the Tomara dynasty in the 8th century. The sound base transformed it gradually to “Delhi.” The name has survived all ups and downs from decades to centuries demonstrating multi-cultural inheritance in the city.
4. What was the first English newspaper in Delhi?
The “Delhi Gazette” is recognized as the foremost English newspaper launched in Delhi. Its first circulation dates back to 1780 during the British colonialism era. This newspaper performed a crucial role in the broadcast of news, information, and official announcements, thereby shaping the communication outlook of Delhi during this epoch.
5. What are the sources of Delhi’s history?
Delhi’s history can be traced through various mediums, such as archaeological findings, inscriptions and historical documents, and also travelers’ accounts. The historical past of Indraprastha is revealed by archaeological excavations while Qutub Minar provides an insight into the ancient history of Delhi. In addition to these, there are texts like Tuzuk-i-Jahangiri or Ain-i-Akbari which tell us about the medieval period under the Mughals’ reign in Delhi. All these different resources help us understand better about Delhi’s glorious past.